FMGS Flight Management Guidance System II
The Flight Management Guidance System (FMGS) contains the following units:
- Two Flight Management Guidance Computers (FMGC)
- Two Multipurpose Control and Display Units (MCDU) (third MCDU optional)
- One Flight Control Unit (FCU)
- Two Flight Augmentation Computers (FAC)
Purpose
The Flight Management and Guidance System (FMGS) provides predictions of flight time, mileage, speed, economy profiles and altitude.
It reduces cockpit workload, improves efficiency, and eliminates many routine operations generally performed by the flight crew.
The Flight Management Guidance System (FMGS) operates as follows:
- During cockpit preparation the flight crew uses the Multipurpose Control and Display Unit (MCDU) to insert a preplanned route from origin to destination. This route includes SID, EN ROUTE, WAYPOINTS, STAR, APPROACH, MISSED APPR, and ALTN route as available from the navigation database.
- Subsequently the system defines a vertical profile and a speed profile, taking into account ATC requirements and performance criteria.
Either FMGC performs all operations, if one FMGC fails.
The FMGS computes the aircraft position continually, using stored aircraft performance data and navigation data. Therefore it can steer the aircraft along a preplanned route and vertical and speed profiles. This type of guidance is said to be "managed".
If the flight crew wants to modify any flight parameter (SPD, V/S, HDG, etc.) temporarily, they may do so by using the various Flight Control Unit (FCU) selectors. The FMGS then guides the aircraft to the target value of this parameter that they have selected. This type of guidance is said to be "selected".
The two available types of guidance, then, are:
Managed guidance, which guides the aircraft along the preplanned route and the vertical and speed/Mach profile. (The FMGS computes the target values of the various flight parameters).Selected guidance, which guides the aircraft to the target values of the various flight parameters the flight crew selects by using the FCU selectors. Selected guidance always has priority over managed guidance.
FCU Flight Control Unit
The FCU located on the glareshield, is the short-term interface between the flight crew and the FMGC. It is used to select any flight parameters or modify those selected in the MCDU. The autopilots and autothrust functions may be engaged or disengaged. Different guidance modes can be selected to change various targets (speed, heading, track, altitude, flight path angle, vertical speed).
MCDU - Multipurpose Control
Two MCDUs are installed on the pedestal for flight crew loading and display of data. The use of the MCDU allows the flight crew to interface with the FMGC by selection of a flight plan for lateral and vertical trajectories and speed profiles. The flight crew may also modify selected navigation or performance data and specific functions of Flight Management (revised flight plan, engine-out, secondary flight plan, etc.). Additional data from peripherals (Centralized Fault Display System (CFDS), ARINC Communication Addressing and Reporting System (ACARS), Air Traffic Service Unit (ATSU)...) can also be displayed. Data that is entered into the MCDU that is illogical or beyond the aircraft capabilities will either be disregarded or will generate an advisory message.
FCU
The Flight Control Unit (FCU) is located on the glareshield and is constituted of three control panels: One for the automatic flight controls and two for the Electronic Flight Instrument System (EFIS). The FCU has two channels, each of which can independently command the central control panel. If one channel fails, the other channel can control all the functions.
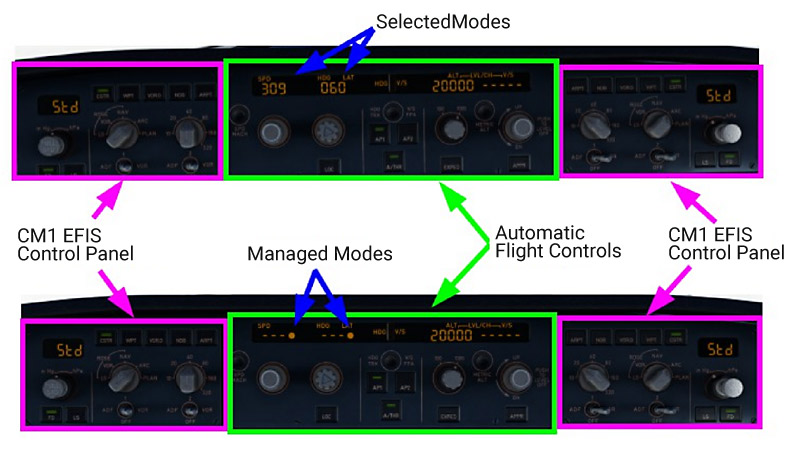
FCU Philosophy
The flight crew can use two types of guidance to control the aircraft in auto flight. One type is managed by the Flight Management Guidance System (FMGS).
The other uses target quantities which are manually entered by the flight crew. When the aircraft uses target quantities from the FMGS (managed guidance), the windows display dashes and the white dots next to those windows light up. When the aircraft uses target quantities, entered by the flight crew (selected guidance), the windows display the selected numbers and the white dots do not light up.
Notice
The altitude window always displays an altitude selected by the flight crew (never dashes).
The FCU has four knobs:
- SPD-MACH
- HDG-TRK
- ALT
- V/S-FPA
The knobs can be rotated, pushed in, and pulled out:
- In order to arm or engage managed guidance for a given mode, the flight crew pushes in the associated knob. If, for example, they push in the HDG knob, they engage or arms the NAV mode.
- In order to engage a selected guidance mode, the flight crew turns the knob to set the desired value, then pulls the knob out to engage the mode with a target value equal to the selected value.
Notice
In managed guidance (lateral, vertical guidance or managed speed), the corresponding window is dashed. Turning a knob without pulling it, displays a value that is the sum of the current target and the turn action value. The display remains 45 s on the HDG/TRK and V/S windows and 10 s on the SPD/MACH window before the dashes reappear. This rule does not apply to the ALT knob/window.
More Info
Click previous page for more info.
Warning
ONLY for Flight-Simulation!